Research Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights 미리보기

Professor Hyobin Yoo’s Research Team at SNU Develops 2D Quantum Material Platform Using Moiré Lattice Superposition
Prof. Hyobin Yoo
Seoul National University College of Engineering has announced that a joint research team led by Professor Hyobin Yoo from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Young-Woo Son (Korea Institute for Advanced Study) and Professor Changwon Park (Ewha Womans University), has successfully developed a two-dimensional (2D) quantum material platform through the superposition of moiré lattices.
Research Highlights Board

MXene-enhanced Ionovoltaic Effect by Evaporation and Water Infiltration in Semiconductor Nanochannels
Prof. Seung Hwan Ko
Professor Ko's research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at SNU has succeeded in developing energy harvesting through water infiltration in semiconductor nanochannels. Additionally, they have efficiently harnessed solar energy using the 2D material MXene, which improves its performance.
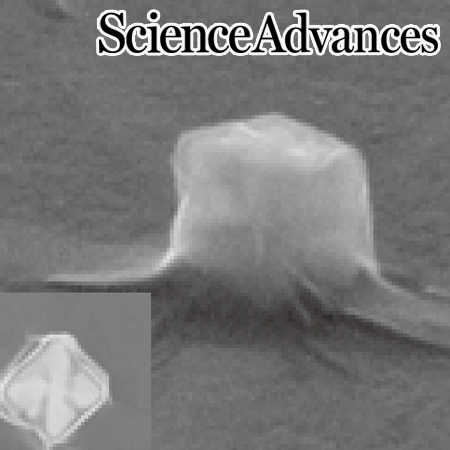
Spin angular momentum-encoded single-photon emitters in a chiral nanoparticle-coupled WSe2 monolayer
Prof. Hong-Gyu Park
Spin angular momentum-encoded single-photon emitters are basic building blocks for the advancement of chiral quantum optics and cryptography.
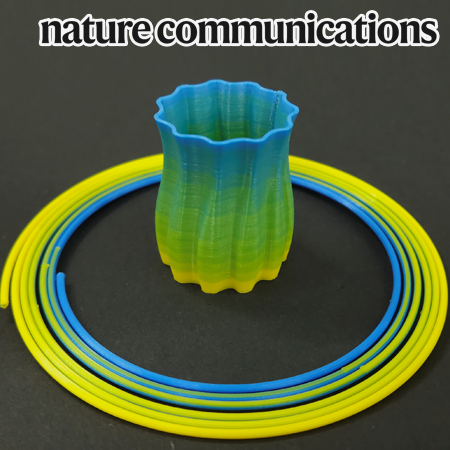

3D Printing with a 3D Printed Digital Material Filament for Programming Functional Gradients
Prof. Howon Lee and Kyu-Jin Cho
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing attracts growing attention as a promising method for creating functionally graded materials.

Metabuli: sensitive and specific metagenomic classification via joint analysis of amino acid and DNA
Prof. Martin Steinegger
Metagenomic taxonomic classifiers analyze either DNA or amino acid (AA) sequences. Metabuli (https://metabuli.steineggerlab.com), however, jointly analyzes both DNA and AA to leverage AA conservation for sensitive homology detection and DNA mutations for specific differentiation of closely related taxa. In the Critical...

Enhancing genome editing in hPSCs through dual inhibition of DNA damage response and repair pathways
Prof. Hyuk-Jin Cha
Precise genome editing is crucial for establishing isogenic human disease models and ex vivo stem cell therapy from the patient-derived hPSCs.

Hypothalamic neuronal activation in non-human primates drives naturalistic goal-directed eating behavior
Prof. Hyung Jin Choi
Professor choi’s research team from the SNU demonstrated that activation of LHAGABA neurons in non-human primate drives naturalistic goal-directed eating behavior and motivation, predominantly for palatable food.

Optogenetic control of mRNA condensation reveals an intimate link between condensate material properties and functions
Prof. Yongdae Shin
Biomolecular condensates, often assembled through phase transition mechanisms, play key roles in organizing diverse cellular activities. The material properties of condensates, ranging from liquid droplets to solid-like glasses or gels, are key features impacting the way resident components associate with one another.
Antibiotic-induced intestinal microbiota depletion can attenuate the acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition via NADPH oxidase 2 and trimethylamine-N-oxide inhibition
Prof. Jung Pyo Lee, Seung Hee Yang
Intestinal microbiota and their metabolites affect systemic inflammation and kidney disease outcomes. Here, we investigated the key metabolites associated with the acute kidney injury (AKI)-to chronic kidney disease (CKD) transition and the effect of antibiotic-induced microbiota depletion (AIMD) on this transition.
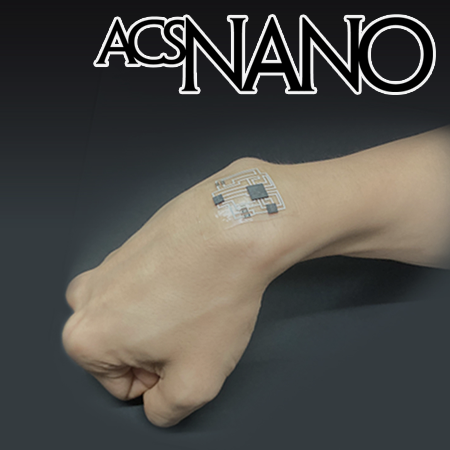

Strain-Insensitive Outdoor Wearable Electronics by Thermally Robust Nanofibrous Radiative Cooler
Prof. Seung Hwan Ko
Stable outdoor wearable electronics are gaining attention due to challenges in sustaining consistent device performance outdoors, where sunlight exposure and user movement can disrupt operations.
Discovery of Terminal Oxazole-Bearing Natural Products by a Targeted Metabologenomic Approach
Prof. Dong-Chan Oh
A targeted metabologenomic method was developed to selectively discover terminal oxazole-bearing natural products from bacteria. For this, genes encoding oxazole cyclase, a key enzyme in terminal oxazole biosynthesis, were chosen as the genomic signature to screen bacterial strains that may produce oxazole-bearing compounds.

Disruption of G-quadruplex dynamicity by BRCA2 abrogation instigates phase separation and break-induced replication at telomeres
Prof. Hyunsook Lee
Dynamic interaction between BRCA2 and telomeric G-quadruplexes (G4) is crucial for maintaining telomere replication homeostasis. Cells lacking BRCA2 display telomeric damage with a subset of these cells bypassing senescence to initiate break-induced replication (BIR) for telomere synthesis.

Phytohormonal regulation determines the organization pattern of shoot aerenchyma in greater duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza)
Prof. Daehee Hwang and Yuree Lee
Airspace or aerenchyma is crucial for plant development and acclimation to stresses such as hypoxia, drought, and nutritional deficiency. Although ethylene-mediated signaling cascades are known to regulate aerenchyma formation in stems and roots under hypoxic conditions, the precise mechanisms remain unclear.

