- Proposing a Minimally Invasive Technique to Address the Risks of Traditional Diagnostic Methods

(From left to right) Jae-Young Bae, PhD; Young-Seo Kim, PhD candidate; Professor Seung-kyun Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Seoul National University; Gyeong-Seok Hwang, PhD; Professor Ju-Young Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, UNIST; Professor Jung Keun Hyun from the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Dankook University Hospital.
The College of Engineering at Seoul National University has announced that Professor Seung-kyun Kang’s research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a biodegradable electronic tent technology that enables brain disease diagnosis using a needle.
The technology, developed by Professor Kang's research team (including Dr. Jae-Young Bae, PhD candidate Young-Seo Kim, and Professor Seung-kyun Kang) in collaboration with researchers from UNIST (Dr. Gyeong-Seok Hwang and Professor Ju-Young Kim) and Dankook University Hospital (Professor Jung Keun Hyun), was published in the internationally renowned journal Nature Electronics on August 5th.
The team's research was driven by the insight that few people would be willing to undergo surgery to implant a brain chip, as recently demonstrated in clinical trials by Neuralink, the neuroscience startup founded by Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla. To implant a brain-computer interface (BCI) device, a dangerous surgery is required to remove part of the skull and insert an electronic chip. Additionally, once the device is no longer needed, it may cause immune reactions, necessitating further surgery to remove it. The research team recognized the need for an alternative to overcome the highly invasive nature of existing methods, which require surgery, for the widespread adoption of bio and brain engineering technologies.
From a clinical perspective, current diagnostic methods for epilepsy and Parkinson's disease necessitate the use of large-area brain electrodes, which require the removal of a significant portion of the skull. This carries the risk of severe side effects such as brain hemorrhage, brain infection, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, and complications like postoperative intracranial hypertension. To alleviate the burden of such surgeries, the research team developed the 'biodegradable electronic tent,' proposing an innovative method for diagnosing brain diseases non-invasively.
Professor Seung-kyun Kang’s research team at Seoul National University, which previously developed a biodegradable brain pressure sensor for wireless brain pressure monitoring and published the results in Nature in 2016, has now developed brain diagnostic technology using electronic devices, cementing its leading role in the global field of biodegradable electronic devices. The joint first authors of this research paper, including Dr. Jae-Young Bae, PhD candidate Young-Seo Kim, and Dr. Gyeong-Seok Hwang, are affiliated with domestic research institutions, highlighting the potential of this research outcome to significantly strengthen South Korea’s technological leadership in medical treatment and research convergence.
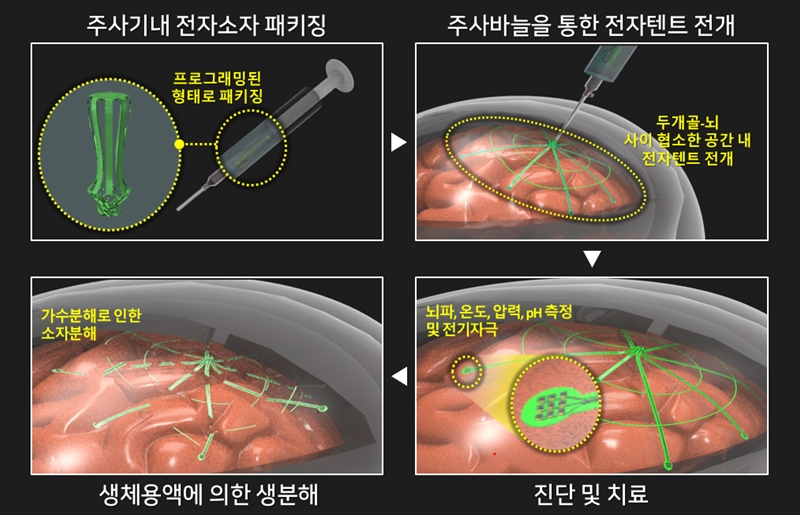
▲ (Figure 1) Process of minimally invasive large-area brain surface electrode insertion using a biodegradable electronic tent
During the development of the 'biodegradable electronic tent technology,' the research team focused on designing the electronic tent to spread evenly and without damage within the narrow space of a few millimeters between the skull and the brain. This was achieved by using biodegradable shape-memory polymers and ultrathin biodegradable inorganic electronic devices. The electronic tent, injected through a small hole in the skull using a needle, unfolds to cover the entire brain over a large area, the size of a palm, within the space between the skull and the brain. Since the device naturally decomposes in the body after the diagnosis is complete, it minimizes the issues associated with residual medical devices causing side effects when left in the body for an extended period, as seen in traditional diagnostic methods for epilepsy and Parkinson's disease.
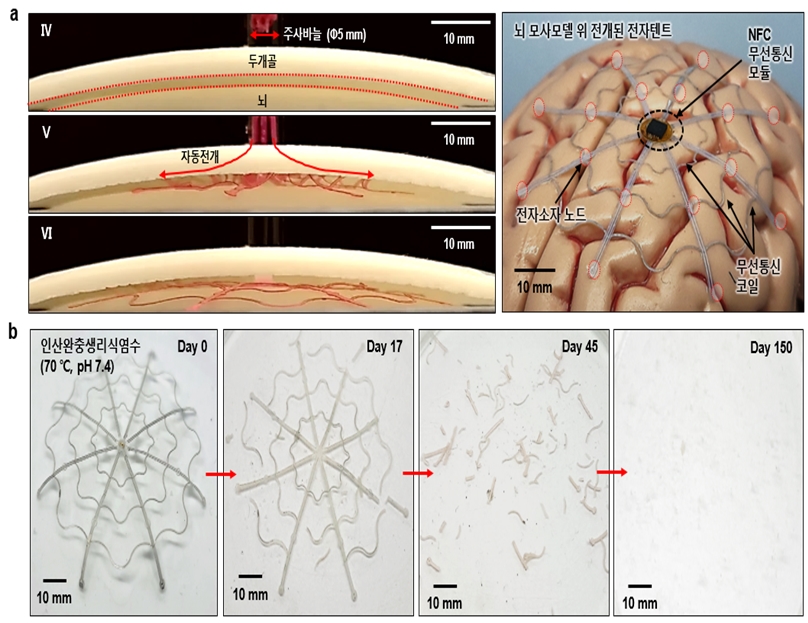
▲ (Figure 2) The process of large-area electronic tent shape recovery and biodegradation within a narrow space
(a) Process of needle insertion and shape recovery of the electronic tent in a skull and brain mimic model
(b) Biodegradation process of the electronic tent in a biomimetic solution
The research team also successfully measured brainwave signals for two weeks after inserting electrodes using the biodegradable electronic tent into the brains of animal models. Additionally, they confirmed the potential for in vivo application by monitoring the biodegradation process of the electronic tent in real-time over an extended period.
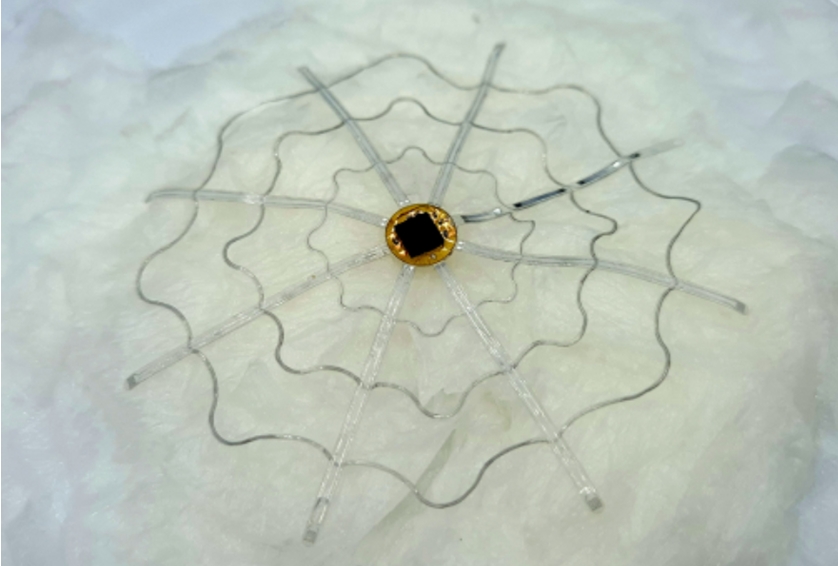

▲ (Figure 3) The electronic tent smoothly attached along the curved surface of brain-mimicking tissue (1% agarose gel)
The biodegradable electronic tent is expected to be utilized in various ways in the medical field in the future. In particular, the biodegradable electronic tent is anticipated to bring significant changes to the diagnostic methods for intractable epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. Unlike the traditional invasive surgical methods that always carry risks, this technology offers a minimally invasive way to insert electronic devices using a needle, providing patients with a better diagnostic environment. Moreover, since the electronic device naturally decomposes in the body after fulfilling its role, it eliminates the need for additional surgeries to remove residual medical devices, making it a safer option for patients.
This technology is also expected to be applicable in diagnosing other brain conditions such as stroke and hydrocephalus. In addition to its applications in diagnosis and treatment, it could also reduce public aversion to the traditional electrode insertion methods used in brain-computer interface (BCI) technologies, such as those tested in Neuralink's brain implantation experiments, thereby enhancing the feasibility of these technologies.
This research was supported by the Nano and Material Technology Development Program (Strategic) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of South Korea.
[Results]
A biodegradable and self-deployable electronic tent electrode for brain cortex interfacing
Jae-Young Bae, Gyeong-Seok Hwang, Young-Seo Kim, Jooik Jeon, Minseong Chae, Joon-Woo Kim, Sian Lee, Seongchan Kim, Soo-Hwan Lee, Sung-Geun Choi, Ju-Yong Lee, Jae-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Sub Kim, Joo-Hyeon Park, Woo-Jin Lee, Yu-Chan Kim, Kang-Sik Lee, Jeonghyun Kim, Hyojin Lee, Jung Keun Hyun, Ju-Young Kim & Seung-Kyun Kang
(Nature Electronics, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01216-x)
[Contact Information]
Professor Seung-kyun Kang, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Seoul National University / 02-880-7162 / kskg7227@snu.ac.kr

