SNU Soft Robotics Research Center has developed a soft wearable hand robot that can aid the hand-disabled by using machine learning algorithm and sensory hardware.
Professor Sungho Jo (KAIST) and Kyu-Jin Cho (Seoul National University), a collaboration research team in Soft Robotics Research Center (SRRC), Seoul, Korea, have proposed a new intention detection paradigm for soft wearable hand robots. The proposed paradigm predicts grasping/releasing intentions based on user behaviors, enabling the spinal cord injury (SCI) patients with lost hand mobility to pick-and-place objects. (The researchers include (KAIST) Daekyum Kim & Jeesoo Ha, (Seoul National University) Brian Byunghyun Kang, Kyu Bum Kim & Hyungmin Choi)
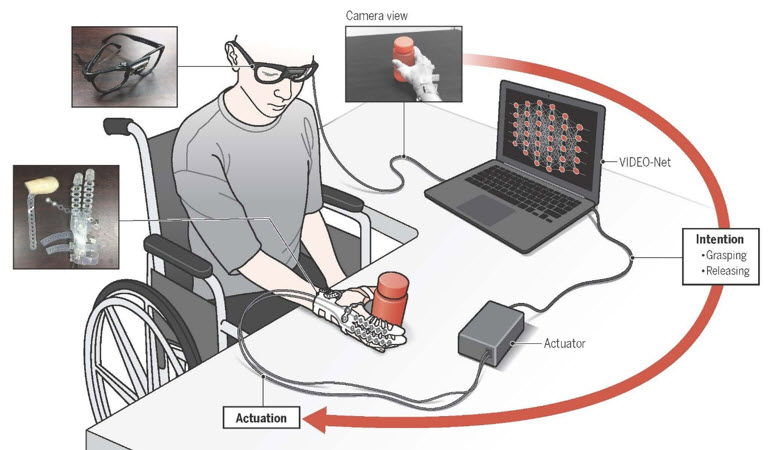
They developed a method based on a machine learning algorithm that predicts user intentions for wearable hand robots by utilizing a first-person-view camera. Their development is based on the hypothesis: user intentions can be inferred through the collection of user arm behaviors and hand-object interactions.
The vision-based machine learning algorithm
The machine learning model used in this study, Vision-based Intention Detection network from an EgOcentric view (VIDEO-Net), is designed based on this hypothesis. VIDEO-Net is composed of spatial and temporal sub-networks, where the temporal sub-network is to recognize user arm behaviors and the spatial sub-network is to recognize hand-object interactions.
An SCI patient wearing Exo-Glove Poly II, (Video of previous version) a soft wearable hand robot, successfully pick-and-place various objects and perform essential activities of daily living, such as drinking coffee without any additional helps.
Their development is advantageous in that it detects user intentions without requiring any person-to-person calibrations and additional actions. This enables the wearable hand robot to interact with humans seamlessly.
The research was published in the 26th issue of Science Robotics as a focus article on January 30, 2019.
Q: How does this system work?
A: This technology aims to predict user intentions, specifically grasping and releasing intent toward a target object, by utilizing a first-person-view camera mounted on glasses.(Something like Google Glass can be used in the future). VIDEO-Net, a deep learning-based algorithm, is devised to predict user intentions from the camera based on user arm behaviors and hand-object interactions. With Vision, the environment and the human movement data is captured, which is used to train the machine learning algorithm.
Instead of using bio-signals, which is often used for intention detection of disabled people, we use a simple camera to find out the intention of the user. Whether the person is trying to grasp or not. This works because the target users are able to move their arm, but not their hands. We can predict the user’s intention of grasping by observing the arm movement and the distance from the object and the hand, and interpreting the observation using machine learning.
Q: Who can benefit from this technology?
A: As mentioned earlier, this technology detects user intentions from human arm behaviors and hand-object interactions. This technology can be used by any people with lost hand mobility, such as spinal cord injury, stroke, cerebral palsy or any other injuries, as long as they can move their arm voluntarily. This concept of using vision to estimate the human behavior
Q: What are the limitations and future works?
A: Most of the limitations come from the drawbacks of using a monocular camera. For example, if a target object is occluded by another object, the performance of this technology decreases. Also, if user hand gesture is not able to be seen in the camera scene, this technology is not usable. In order to overcome the lack of generality due to these, the algorithm needs to be improved by incorporating other sensor information or other existing intention detection methods, such as using an electromyography sensor or tracking eye gaze.
Q: To use this technology in daily life, what do you need?
A: In order for this technology to be used in daily life, these devices are needed: a wearable hand robot with an actuation module, a computing device, and glasses with a camera mounted. We aim to decrease the size and weight of the computing device so that the robot can be portable to be used in daily life. So far, we could find compact computing device that fulfills our requirements, but we expect that neuromorphic chips that are able to perform deep learning computations will be commercially available.
■ Professor Kyu-Jin Cho
Professor Kyu-Jin Cho is the director of the Soft Robotics Research Center and Biorobotics Lab in Seoul National University. He received the IEEE Robotics and Automation Society Early Career award in 2014 for his achievement in the field of soft robots and bio-inspired robots. In 2015, He developed the water strider robot published in the journal Science, which was covered by over 300 media, including NY Times, BBC and NBC. In 2016, he presented the Exo-Glove Poly, a glove-like soft robot that helps people with disabilities in their daily lives, at the AAAS Annual Convention. In April of the same year, he won the Soft Robot Challenge with the robot named 'SNUMAX' which was held in Pisa, Italy for the first time. He is leading the Soft Robotics Research Center to develop soft robotic technologies which will bring robotics closer to people.

